

Hawaii and Washington have the highest estate tax top rates in the nation at 20 percent. Inheritance taxes are remitted by the recipient of a bequest and are thus based on the amount distributed to each beneficiary. Maryland is the only state to impose both a state estate tax rate and a state inheritance tax rate.Įstate taxes are paid by the decedent’s estate before assets are distributed to heirs and are thus imposed on the overall value of the estate. Twelve states and the District of Columbia impose estate taxes and six impose state inheritance taxes. However, gifting that occurs within a few years of death is often considered as having happened in contemplation of death, so it might not be enough to help your beneficiary avoid a significant tax bill.In addition to the federal estate tax, with a top rate of 40 percent, some states levy an additional state estate tax or state inheritance tax. You are provided with an annual exemption amount of how much money you can give to an individual before it is taxed, and you can continue to give that amount on an annual basis until you have reached your lifetime cap. Gifting may also help you enable beneficiaries to avoid inheritance taxes in their state. These types of transactions are often exempt from inheritance taxes to help encourage charitable contributions. Leaving inheritances to charities is a potential way to avoid the inheritance tax consequences that might otherwise befall a beneficiary. If you have beneficiaries that live in one of the states that imposes inheritance taxes – including New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Kentucky, Iowa, and Nebraska – it is important for you and/or them to work with an experienced estate planning attorney in that jurisdiction to get a better understanding of what the potential tax liabilities for the beneficiary might be. The amount of tax that is to be paid is generally determined by the value of the inheritance.Ĭan your beneficiary avoid the inheritance tax? While a decedent’s estate is responsible for any potential estate tax liabilities on both the federal and state level, the individual beneficiary is responsible for any inheritance tax they might face. There may be an exemption amount for other related relatives such as cousins or siblings, but often unrelated individuals are subject to higher inheritance taxes.

And may also exclude other direct family members like children. Generally, states that have an inheritance tax exclude surviving spouses.
#Inheritance tax ny how to
New York does not have an inheritance tax, but other states do and it is important to take the potential impact of an inheritance tax on a beneficiary when determining how to distribute your assets.Īn inheritance tax is just that: a tax liability on a person’s inheritance.
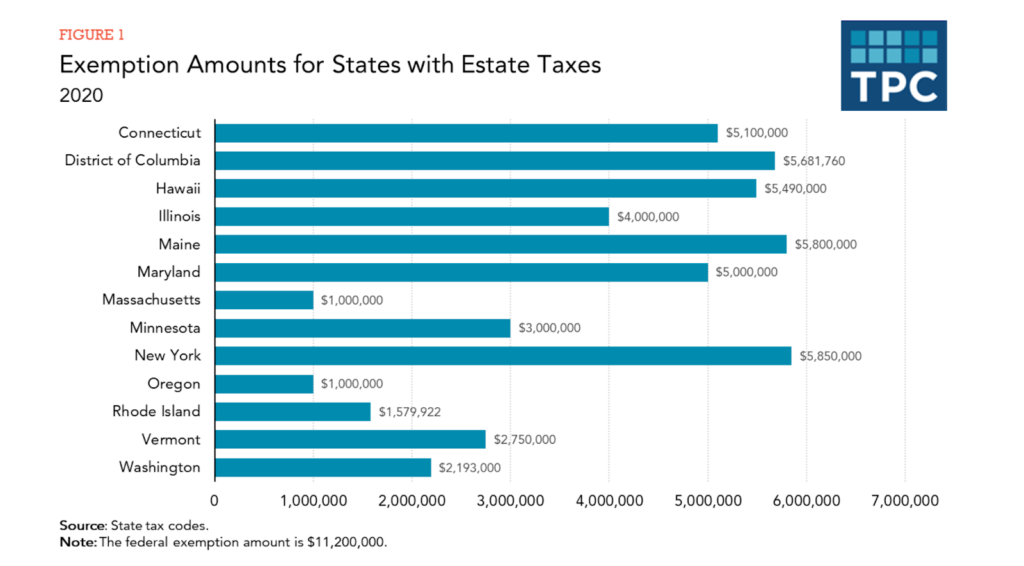
That means any estates worth over that amount in New York are subject to the state estate tax even if they are no longer subject to the federal estate tax.īut what about the inheritance tax? The inheritance tax is not as well known, due in part to the fact that it is less common. In New York, the current state tax exemption is approximately half of the new federal exemption amount and sits at $5,250,000. However, many states also have estate taxes – including New York. The new tax bill doubles the exemption, and many people will not have to worry about the federal estate tax at the moment. One of the most common tax considerations when it comes to estate planning is the estate tax itself, a federal tax applied to estates valued at over a certain amount. However, individuals inheriting from you may also need to be concerned with important considerations like the potential tax consequences of being a beneficiary. There are a lot of considerations when it comes to comprehensive estate planning, not the least of which is choosing the vehicles you will use in your estate planning strategy to meet your needs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
